Evaluating the effectiveness of e-cigarettes compared with usual care for smoking cessation when offered to smokers at homeless centres: protocol for a multi-centre cluster-randomized controlled trial in Great Britain
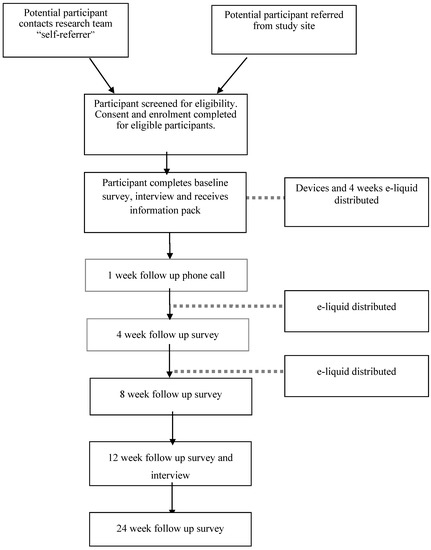
Smoking is extremely common among adults experiencing homelessness, but there is lack of evidence for treatment efficacy. E-cigarettes are an effective quitting aid, but they have not been widely tested in smokers with complex health and social needs. Here we build upon our cluster feasibility trial and evaluate the offer of an e-cigarette or usual care to smokers accessing a homeless centre.
Electronic cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy among patients with COPD: protocol for an open-label two arm randomized controlled pilot trial
Smoking cessation is the most effective means of slowing the decline of lung function associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). While effective smoking cessation treatments are available, they are underutilized and nearly half of people with COPD continue to smoke. By addressing both nicotine and behavioral dependence, electronic cigarettes (EC) could help people with COPD reduce the harm of combustible cigarettes (CC) through reductions in number of Cigarettes per Day (CPD) or quitting CC completely. The purpose of this pilot study is to identify barriers and facilitators to the use of and assess the preliminary effectiveness of EC as a harm reduction strategy among people with COPD.
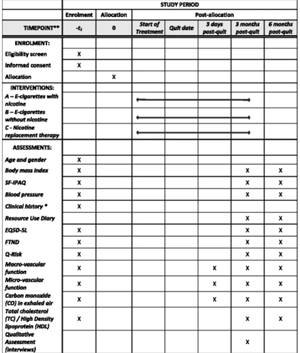
Effectiveness and safety of nicotine patches combined with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) for smoking cessation: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Evidence indicates e-cigarettes can help people quit smoking; however, more confirmatory trials are needed. To date, no trials have evaluated the effectiveness and safety of combining nicotine patches with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) for smoking cessation. This study is a pragmatic, three-arm, community-based, single-blind, randomised trial undertaken in New Zealand.
The effectiveness and safety of combining varenicline with nicotine e-cigarettes for smoking cessation in people with mental illnesses and addictions: study protocol for a randomised-controlled trial
Smoking rates are higher in New Zealand (NZ) adults with mental illnesses and alcohol and other drug (AOD) addictions, compared to the overall population. Quit attempts using "gold standard" smoking cessation treatments often fail in people with these conditions, so more flexible treatment regimens that adapt to a person's responsiveness to treatment are worth investigating. The STATUS trial aims to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of combining varenicline with nicotine e-cigarettes for smoking cessation among varenicline non-responders in treatment for mental health illnesses and/or AOD addictions.
Tobacco Harm Reduction with Vaporised Nicotine (THRiVe): The Study Protocol of an Uncontrolled Feasibility Study of Novel Nicotine Replacement Products among People Living with HIV Who Smoke
Smoking is a leading cause of morbidity and premature mortality among people living with HIV (PLHIV), who have high rates of tobacco smoking. Vaporised nicotine products (VNPs) are growing in popularity as a quit aid and harm reduction tool. However, little is known about their acceptability and use among PLHIV. Using a pragmatic, uncontrolled, mixed methods design this exploratory clinical trial aims to examine the feasibility of conducting a powered randomised clinical trial of VNPs as a smoking cessation and harm reduction intervention among vulnerable populations, such as PLHIV who smoke tobacco.
Smokers making a quit attempt using e-cigarettes with or without nicotine or prescription nicotine replacement therapy: Impact on cardiovascular function (ISME-NRT) - a study protocol
The estimated number of cigarette smokers in the world is 1.3 billion, expected to rise to 1.7 billion by 2025, with 10 million smokers living in the U.K. Smoking is the leading, preventable death-cause worldwide, being responsible for almost 650,000 deaths in the E.U. annually. A combination of pharmacological interventions, including nicotine replacement therapy, bupropion and varenicline, and behavioural support is the most effective approach to smoking cessation.
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use
Although smoking cessation is currently the only guaranteed way to reduce the harm caused by tobacco smoking, a reasonable secondary tobacco control approach may be to try and reduce the harm from continued tobacco use amongst smokers unable or unwilling to quit. Possible approaches to reduce the exposure to toxins from smoking include reducing the amount of tobacco used, and using less toxic products, such as pharmaceutical, nicotine and potential reduced-exposure tobacco products (PREPs), as an alternative to cigarettes.
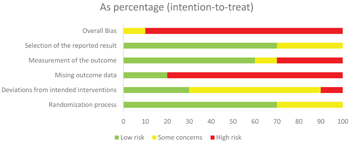
Efficacy and safety of electronic cigarettes as a smoking cessation intervention: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
This systematic review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluated the efficacy and safety of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes, ENDS) in helping people who smoke to achieve abstinence compared with electronic non-nicotine delivery systems (ENNDS, no nicotine) or any smoking cessation comparator treatment or combination of treatments at 24-26 weeks and at 52 weeks.
Research
Reports
Featured Posts
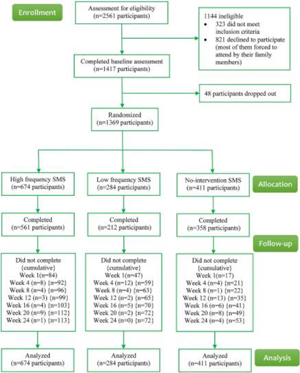
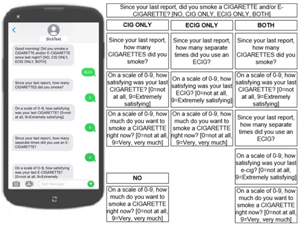
Effectiveness of a text-messaging-based smoking cessation intervention ("Happy Quit") for smoking cessation in China: A randomized controlled trial